The molecular structure of Nafuredin
Click on the image above to interact with the 3D model of the Nafuredin structure
Nafuredin
Discovery, producing organism and structure (1-4)
Nafuredin was isolated from a culture broth of the fungal strain FT-0554 and recognized as an inhibitor of helminth NADH-fumarate reductase. Its target was revealed to be complex I (NADH-quinone oxidoreductase), and it was identified as a selective inhibitor of helminth complex I. Nafuredin showed anthelmintic activity against Haemonchus contortus in in vivo studies. The structure of nafuredin was elucidated as β,γ-epoxy-δ-lactone with a branched side chain, and its absolute configuration was revealed synthetically. Nafuredin is biosynthesized from a nonaketide and four methionines (branched methyl carbons) (2).
Physical data
White powder. C22H32O4; mol wt 360.50. Sol. in DMSO, EtOH, EtOAc, CHCl3. Insol. in H2O, hexane.
Biological activity (1,4)
1) Effects on electron transport enzymes
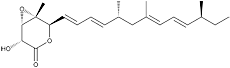
Nafuredin
2) Kinetic analysis of nafuredin inhibition of A. suum complex I
The inhibition is non-competitive with NADH (Ki=8.1 nM) and competitive with
rhodoquinone (Ki=8.3 nM).
4) Toxicity
There were no signs of side effects or reduction of body weight during the testing period
in either sheep (2 mg/kg p.o.) or mice (50 mg/kg p.o. and i.p.).
5) Antimicrobial activity (10 μg/6 mm disc, paper disc method)
References
1. [768] S. Ōmura et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 60–62 (2001)
2. [772] H. Ui et al., J. Antibiot., 54, 234–238 (2001)
3. [776] D. Takano et al., Tetrahedron Lett., 42, 3017–3020 (2001)
4. [785] K. Shiomi et al., Bioscience and Industry, 59, 37–38 (2001)
5. [787] D. Takano et al., Org Lett., 3, 2289–2291 (2001)