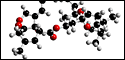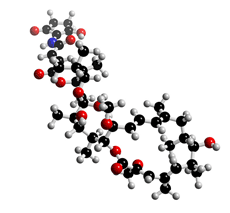
The molecular structure of Setamycin
Click on the image above to interact with the 3D model of the Setamycin structure
Setamycin
Discovery, producing organism and structure (1-8)
Setamycin was isolated from a culture broth of the actinomycete strain KM-6054 and recognized to possess antimicrobial and nematocidal activity (1,2). Later, bafilomycin (3,4), a Golgi protein transfer inhibitor was found, and bafilomycin B1 was identified as being identical in structure to setamycin. The taxonomic study of the producing strain led us to establish a new genus of Kitasatospora setae (4–6).
Physical data
Yellow powder. C44H65NO13; mol wt 815.45. Sol. in MeOH, EtOH, benzene. Insol. in H2O, hexane.
Biological activity (1,2)
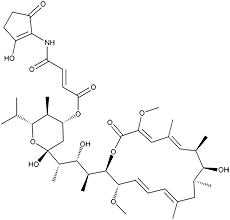
Setamycin
1) Antimicrobial spectrum (1)
2) Setamycin has nematocidal activity (pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus lignicolus) with an IC50 value of 10 µg/ml2).
References
1. [216] S. Ōmura et al., J. Antibiot., 34, 1253–1256 (1981)
2. [383] K. Otoguro et al., J. Antibiot., 41, 250–252 (1988)
3. G. Werner et al., J. Antibiot., 37, 110–117 (1984)
4. [224] S. Ōmura et al., J. Antibiot., 34, 1633–1634 (1981)
5. [245] S. Ōmura et al., J. Antibiot., 35, 1013–1019 (1982)
6. [721] Y. Takahashi et al., Zent. bl. Bacteriol. 289, 263-284 (1999)
7. [721] G. Michael et al., J. Antibiot., 50, 1073–1077 (1997)
8. E. Ohta et al., Tetrahedron Lett., 42, 4179–4181 (2001)